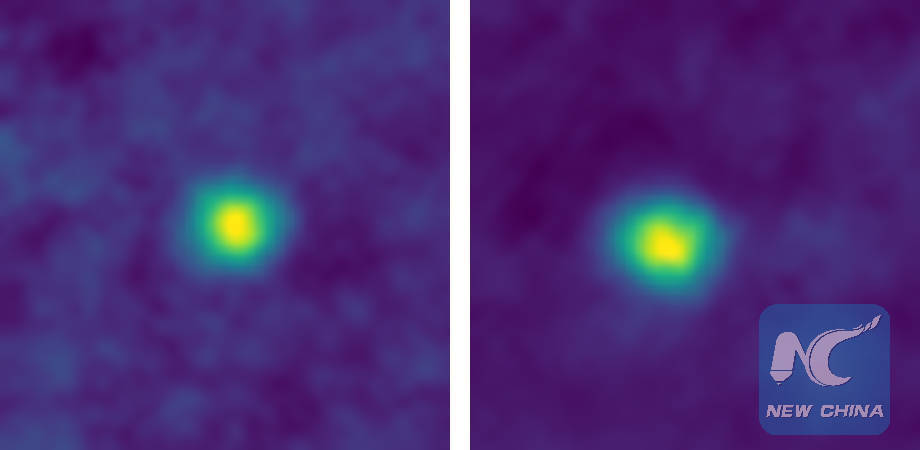
With its Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), New Horizons has observed several Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs) and dwarf planets at unique phase angles, as well as Centaurs at extremely high phase angles to search for forward-scattering rings or dust. These December 2017 false-color images of KBOs 2012 HZ84 (left) and 2012 HE85 are, for now, the farthest from Earth ever captured by a spacecraft. They're also the closest-ever images of Kuiper Belt objects. (Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI)
LOS ANGELES, Feb. 11 (Xinhua) -- The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has announced that its New Horizons spacecraft has recently taken the farthest ever images from Earth, breaking a previous record set by Voyager 1's "Pale Blue Dot" taken in 1990.
New Horizons is the first NASA spacecraft to fly by Pluto and the fifth to speed beyond the outer planets. So many of its activities set distance records.
According to a statement by NASA, the probe snapped a false-color image of a group of stars known as "Wishing Well" on Dec. 5, 2017 while it was 6.12 billion km away from Earth and en route to the Kuiper Belt, a circumstellar disk surrounding the solar system.
NASA said the image, captured by New Horizons's Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), was "for a time, the farthest image ever made from Earth."
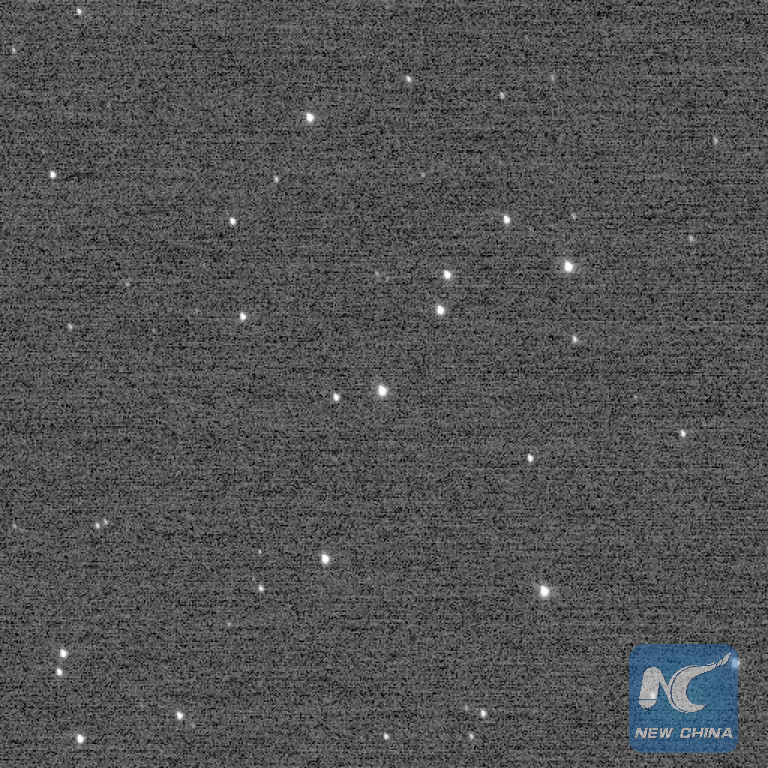

The Wishing Well star cluster was the farthest picture taken for two hours on December 5th. About two hours later, New Horizons later broke the record again. (Credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI)
The previous record holder for the farthest picture was NASA's Voyager 1, which shot the famous "Pale Blue Dot" image of Earth on Feb. 14, 1990. Some 6.06 billion km from Earth, Voyager 1 took the picture as part of a composite of 60 images looking back at the solar system.
"LORRI broke its own record just two hours later with images of Kuiper Belt objects 2012 HZ84 and 2012 HE85, further demonstrating how nothing stands still when you're covering more than 1.1 million kilometers of space each day," NASA said in the statement.
"Mission scientists study the images to determine the objects' shapes and surface properties, and to check for moons and rings. The spacecraft also is making nearly continuous measurements of the plasma, dust and neutral-gas environment along its path," it added.
New Horizon's principal investigator Alan Stern said in the statement that the unmanned, piano-sized probe, launched in 2006, "has been a mission of firsts -- first to explore Pluto, first to explore the Kuiper Belt, fastest spacecraft ever launched."
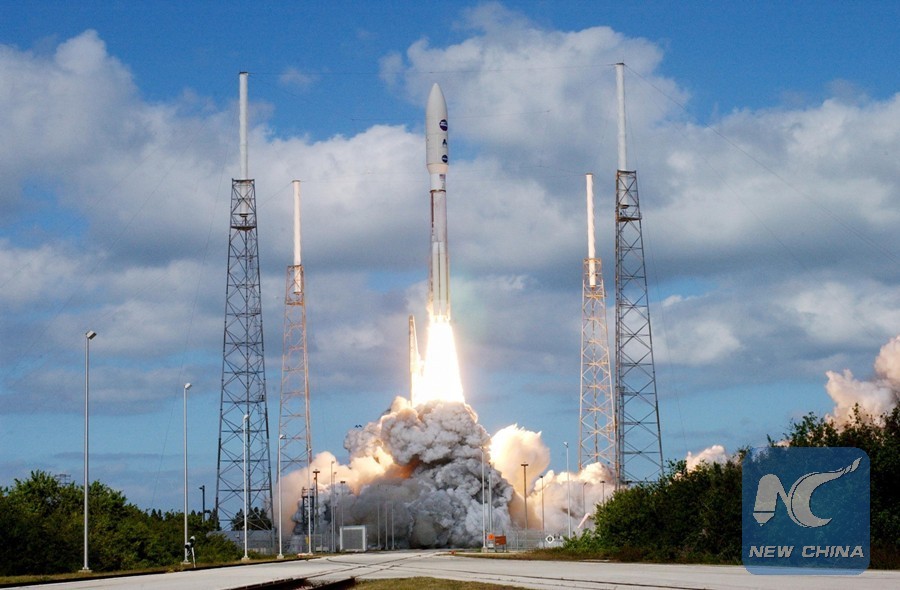

The photo handed out by NASA shows the unmanned probe, New Horizons, blasting off from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, the United States, Jan. 19, 2006. (Xinhua Photo/NASA)
NASA said New Horizons is in the hibernation mode now, awaiting its next adventure due Jan. 1, 2019, at which time it will fly past an Kuiper Belt object (KBO) named 2014 MU69. It will be the farthest planetary encounter in history.
Located about 1 billion miles (1.61 billion kilometers) beyond Pluto, which New Horizons famously flew by in July 2015, 2014 MU69 was discovered in June 2014 by scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope.
Beginning in 2017, New Horizons' extended mission in the Kuiper Belt aims to complete the reconnaissance of the solar system. NASA said the spacecraft is expected to observe at least two-dozen other KBOs, dwarf planets and "Centaurs," former KBOs in unstable orbits that cross the orbits of the giant planets.

